In 2012 TITAN launched a new entity called GAEA – Green Alternative Energy Assets LTD in Cyprus, as a joint venture with the American specialized Environmental Evolution (E2) Company with the intention of becoming the alternative fuels solution provider for the Southeastern Europe and Eastern Mediterranean business units of the Group. The first operational subsidiary was established in Bulgaria in mid-2012 to provide solutions, consulting and environmental services, including the removal and pre-treatment of post use consumer and commercial/industrial wastes for replacing conventional fossil fuels and raw materials primarily to TITAN’s Zlatna Panega cement kilns, as well as to other large industrial furnaces and utilities in the region. GAEA Bulgaria offers its waste solutions services to both public and private local entities, through a service agreement with Zlatna Panega, allowing it to operate as an independent alternative fuel processing facility in the Lovech region.
Processing of waste and production of PEF (Processed Engineered Fuel) takes place in the PEF installation, the first of its kind within the TITAN Group, commissioned at the end of 2011. PEF is a fuel of uniform and constant quality made from various non-recyclable waste materials with variable quality and composition. Its main feed stock material comes from the Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) deposited in the Sofia landfill, while the PEF is enhanced by the use of other carefully selected High Heat Value (HHV) industrial, commercial or biomass by-products.
In general, many and varied by-product materials have been used for the production of PEF. The main feed stock is RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) that is delivered from three material recovery facilities sorting the MSW of the Suhodol landfill in Sofia. RDF contains mainly non-recyclable plastics, paper, textile, foils and other burnable materials. The quality of RDF usually varies from day to day and delivery to delivery, so it needs to be standardized to satisfy the energy needs of the clinker production process.
In 2012, a total volume of 13,130 tons of RDF was processed through the installation. In order to improve the NCV (Net Calorific Value) additional quantities of 2,440 tons of local Biomass (rice husks, sunflower husk and saw dust) and 470 tons of sourced HHV materials (textile, plastics and rubber) were used as correctives. Additionally, 89 tons of HHV hazardous materials were processed and co-incinerated in the kiln of the cement plant.
In parallel to the benefits accrued to the Zlatna Panega plant, valuable services have also been provided to local society in terms of co-incinerating materials that are subject to a special regime by the authorities, such as cigarettes and out of date identification papers. Moreover, nearly 10,000 tons of CO2 have been saved through this environmentally friendly fuels substitution activity.
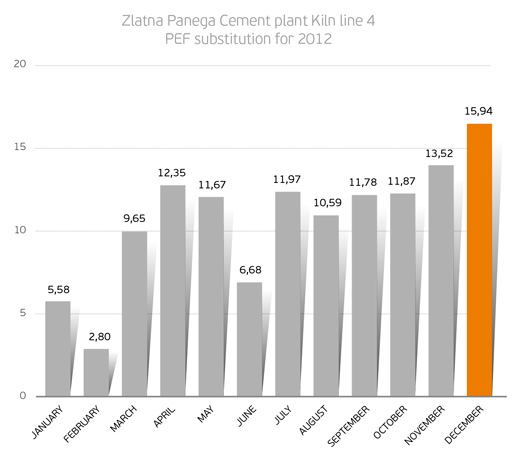
Zlatna Panega and GAEA have successfully embarked on this new and challenging activity, achieving many significant targets within 2012 and reaching up to 25% total substitution rate at the end of the year (PEF and tires together). However, much remains to be learned. The main challenge is to gain further experience in the production of a uniform fuel by using many different materials of inconsistent quality. In 2013, GAEA and the Zlatna Panega plant intend to gradually increase the feeding of PEF by making it even more stable and convenient for use.